Oxygen is a vital molecule that many organisms need as fuel for survival. What occurs in the body and the many activities oxygen is a prime accelerator and catalyst of, is not very well known among the public. For most, oxygen is essential because the lack of it triggers cellular senesces and eventually death. While the intricate knowledge of oxygen and its significant role in metabolic activity may not seem necessary in everyday life, however, to fathom the gravitational consequences of OxyCure, it is necessary. Having a concept about cellular respiration is critical here, otherwise, OxyCure might seem like nothing more than breathing oxygen, when in reality, it is groundbreaking.
The role of oxygen in cell survival
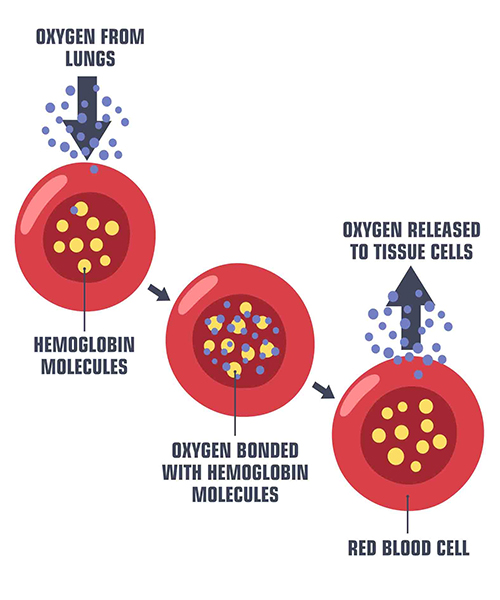
Now, in short, cells require oxygen to release energy used to fuel metabolic activity. The energy comes from food, initially, but to break down food into units of energy that cells can exhaust for survival, oxygen is compulsory. So how does oxygen come from the lungs to become a complicit character in the life of every cell? Once oxygen is inhaled into the lungs as a result of the different pressures between the lungs and the atmosphere, oxygen diffuses to the blood through the thin membrane of the alveoli.
The process is known as cellular respiration because it is technically respiration under a cellular level. In other words, cells take oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The alveoli are designed to be a very thin membrane to facilitate the diffusion of oxygen and contact of gases between the blood and the molecules trapped in it.
Diffusion is a process by which molecules move from regions of high concentrations to regions of low concentration. The oxygen is then transported in the blood carried by hemoglobin and plasma to various tissues and cells.
The detailed process of cellular respiration
The process, in essence, is divided into two stages, glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle. The two processes transform food into carbon dioxide and high-energy molecules. To word it differently, respiration basically transform food that is an organic compound to an inorganic compound that is carbon dioxide.
Consequently, after their release, high-energy molecules will then transport their equally energetic electrons in an electron transport chain that takes place in the powerhouse of the cell, the mitochondria.
To make things simple, what occurs in the electron transport chains is that the high-energy electrons will be transported to a set of proteins. The process passes the high-energy of electrons to molecules known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a form of energy the cell can utilize. Once electrons have lost all their energy, they will find their way to the final factor of this process, oxygen, and form water molecules.
The respiration equation is the following:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ———> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + (a lot of) ATPs
Oxygen is necessary for the electron transport chain that essentially produces around 38 molecules of ATP. Without oxygen, cells get into senesces and begin deteriorating until their eventual death.
What happens when there is not enough oxygen
Oxygen levels often decrease after surgery, such as hair transplants. The body loses energy and cannot sustain the myriad activities whether the usual activities or the recent post-surgery wounds and symptoms. Therefore, by increasing oxygen content in the blood, OxyCure accelerates the versatile range of metabolic activity in the body. Otherwise, when there is a shortage of oxygen, the body groups functions into categories of necessary and dispensable. Therefore, processes such as hair growth, collagen production, etc, are considered secondary functions that can be terminated for the time being.